下载
1
03-2015, Rev. 0315
www.te.com
© 2015 Tyco Electronics Corporation,
a TE Connectivity Ltd. company.
Catalog and product specification according
to IEC 61810-1 and to be used only together
with the ‘Definitions’ section.
Catalog and product data is subject to the
terms of the disclaimer and all chapters of
the ‘Definitions’ section, available at
http://relays.te.com/definitions
Catalog, product data, ‘Definitions’ section,
application notes and all specifications are
subject to change.
Automotive Applications
Automotive Relays
Application Notes
Typical Automotive Applications
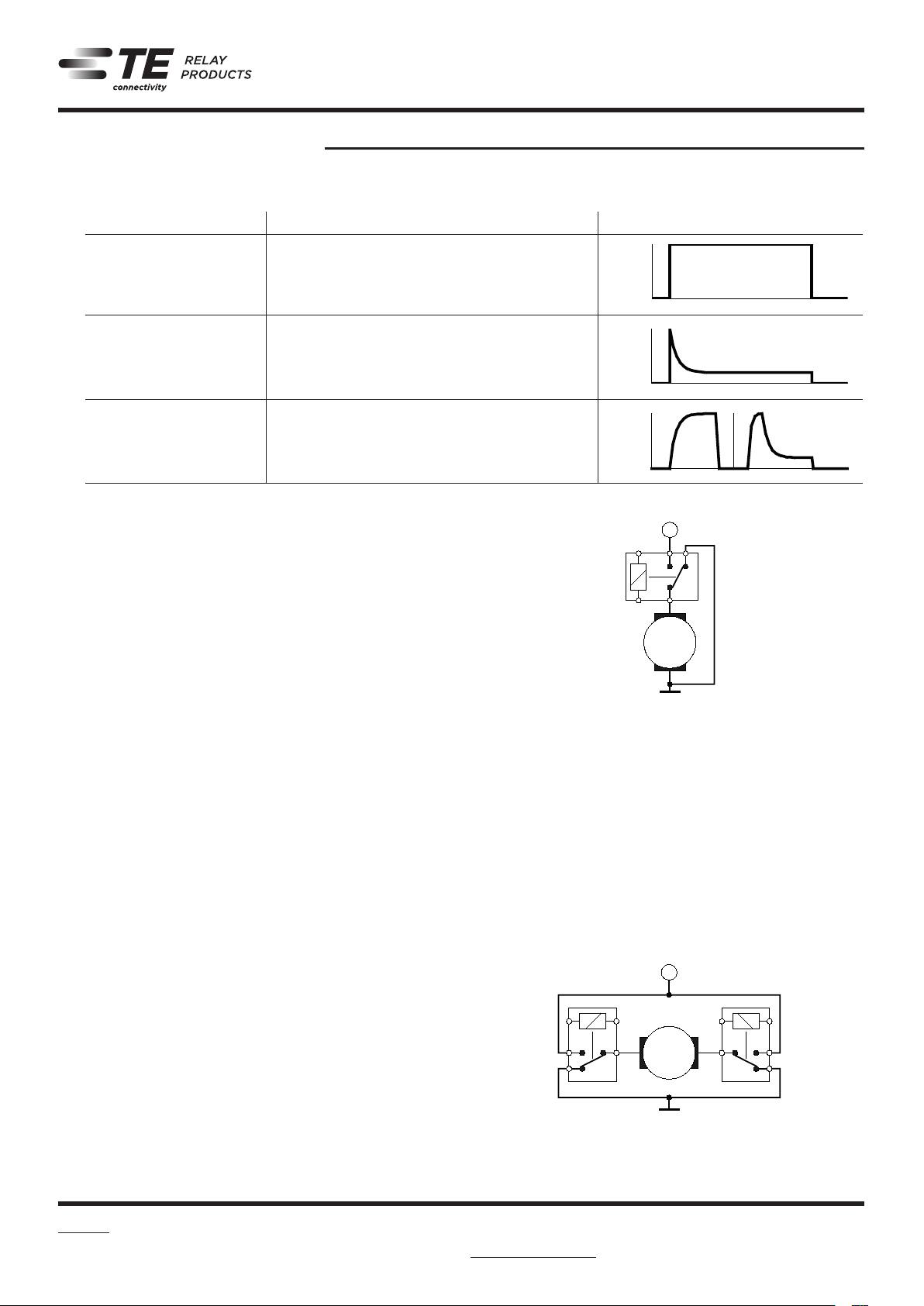
Load Application examples Typical current curve
Resistive Loads - Heatings
(rear window heating, seat heating
glow plug, air/water preheating)
Capacitive Loads - Lamps
(front and rear beam, fog lights, flasher)
- Filter capacitors in electronic modules
(engine management module, ABS module)
Inductive Loads - Solenoids
(vales, clutches, relay coils)
- Motors and pumps
(power window, central lock, cooling fan)
Introduction
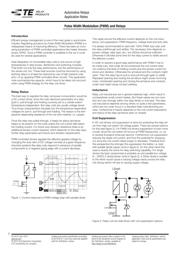
The range of applications can be classified into resistive loads,
capacitive loads and inductive loads. The current curve of resis-
tive loads is specified by the load voltage and load resistance.
Capacitive loads have a high inrush current and a low steady
current. Therefore lamps are counted to the capacitive loads,
because the cold filament has a significantly lower resistance,
than the hot filament. Inductive loads are characterized by an
exponential current increase and a remarkable switch off arc,
induced by the demagnetization of the magnetic circuit of the
load. Power supply relays (clamp relays) can switch or feed
a mixture of different loads.
The circuit design of resistive and capacitive loads is usually a
simple switch on and switch off. Motor load circuits are often
more complex. The most typical circuits are described hereafter.
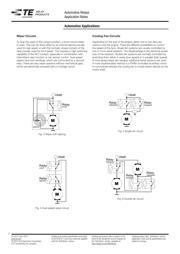
Short-Circuit Brake
The short-circuit brake is used, wherever an electric motor must
be braked (e.g. wiper). The short-circuit brake transforms the
rotational energy of the motor into electrical energy. The short-
circuit brake can be critical at higher load voltages. If the switch-
off arc does not extinguish during the transition time of the
movable contact, the arc creates a direct shortage of the power
source. Particularly in 24VDC systems, the resulting extremely
high arc current could cause almost instantly severe damage to
the contacts and could destroy the entire relay.
Fig. 1 Short-circuit brake
Motor-Reverse Circuit (H-Bridge)
The H-bridge is used to operate a motor in two directions
(e.g. door lock, steering lock, power window,
seat adjustment, etc.). The operation time is typically
very short compared to the thermal time constant of
the relay (e.g. door lock <1s, power window <10s).
This means, H-bridge relays must be designed for
high current-switching-capability, but not for high
current-carrying-capability. Higher load voltages can
be critical, due to possible short-circuit-arcs (see also
short-circuit brake).
Fig. 2 H-bridge
time
current
time
current
time
current
Solenoid
Motor
M
Ubatt
Rela
y
M
Ubatt
Relay
turn right
Relay
turn left